For as long as we can remember, meat eating has been a fundamental part of human history.
But recently, there has been a lot of talking about what cultivated meat is and how it is transforming the narrative of the meat industry.
The cultivated meat market is still in its infancy and will be worth US$ 25 billion by 2030. The value of cultivated meat in the Asia-Pacific region is expected to exceed 18 billion dollars by 2030.
Health-focused messages, plant-based meat options, and animal welfare drive this food innovation’s appeal.
The cultivated market trends resemble a tech landscape, attracting multi-million dollar investments in growing low-cost meat in labs with a small carbon footprint.
What is Cultivated Meat?
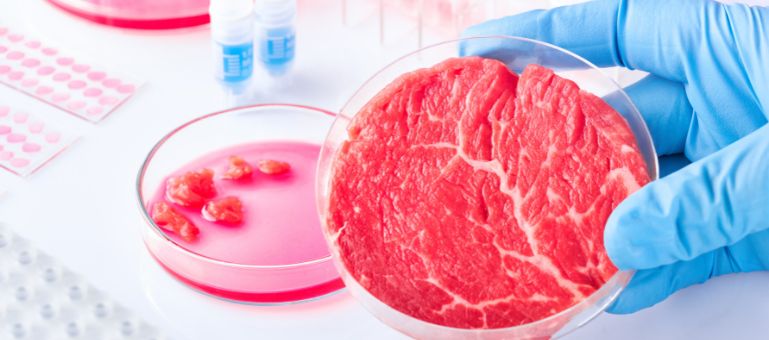
Across science and innovation, significant advances grew momentum for cultivated meat, also known as cellular meat. Cultivated meat is genuine animal meat that doesn’t require animals to be slaughtered the way traditional meat does.
Cultivated meat is a bit dense and on the smaller side – well browned on the outside, and the flavor is full and savory.
Also, there is a clear difference between plant-based meat and cell-grown meat. Cultivated meat doesn’t fall under the vegan food category because cultured cells are taken from animals. At the same time, plant-based meat is made from plant protein.
The idea is to develop humane meat, and according to the top trends in the meat sector, it is a new wave of future to create more ecologically friendly options.
How is Cultivated Meat Produced?
To produce lab-grown meat and poultry, a sample of stem cells is taken from a live animal. This process is much less harmful than killing animals for their meat.
The manufacturing process requires acquiring and banking stem cells from animals. Commonly known as cultivators, these cells have high density and volume.
These cells have an oxygen-rich cell culture in a controlled environment to ensure essential nutrients, such as amino acids, glucose, vitamins, and inorganic salts.
The scaffolding of these structures is then harvested and prepared, and it generally takes between 2-8 weeks before they are packaged into final cell-based meat products.
Various technologies are involved in producing lab-grown cultivated meat, such as bioprocess design, tissue engineering, cell lines, cell culture media, and 3D cell culture platforms.
Scaling up to make cultivated meat in more extensive production facilities will reduce emissions compared with conventional beef production. However, the actual climate impacts are yet to be determined.
Benefits of Cultivated Meat
As the foodtech continues to evolve, scientists have been able to grow real meat in labs. Cultured meat is considered to be relatively cruelty-free and environmentally conscious.
Identical to conventional meat, tender and chewy, it is expected to benefit the food industry.
Tempted? Let’s explore the benefits of lab-grown meat.
Less Likely to Cause Foodborne Illnesses

According to the World Health Organization, unsafe food causes 600 million foodborne diseases and 420,000 deaths. It is estimated that 33 million years of healthy lives are lost globally due to eating unsafe food.
Pathogen exposure is unavoidable in slaughterhouses, but lab grown meat reduces exposure to potential pathogens that cause illness.
The controlled setting ensures safer and more hygienic meat production, reducing the threat of foodborne illnesses.
According to a study by the Good Food Institute, commercially cultivated meat production will reduce illness by eliminating antibiotics, ensuring a more sustainable and safer consumption.
Environment Advantages

Agricultural production is estimated to account for 40 percent of global food system emissions, which are believed to account for 35 percent of total greenhouse gas emissions—the agriculture sector shares global GHG emissions of about 12.3%.
Leaping from pharma to food, one of the biggest goals of the industry is to use energy-intensive production for lab-grown meat using primarily food-grade ingredients or cultures.
As stated in the Good Food Institute study, if cultivated meat is produced using renewable energy, it could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 92% and land use by up to 90% compared to conventional beef.
Also, according to recent studies published in Oxford Economics report, cultivated meat can lower the country’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions compared to livestock farming and transportation of meat.
However, the comparison of farmed and cultivated meat based on greenhouse gas emissions needs to be better accounted for in the standard measure.
It will depend on what level of sustainable energy generation can be achieved. Scientists and food experts are further uncovering the facts about cell-based meat’s environmental effectiveness.
No/Fewer Antibiotics

According to a research study, antibiotics are administrated into food-producing animals to facilitate antibiotic resistance.
Still, it may result in a huge and negative impact on public health and food safety regarding drug toxicity, immunopathological diseases, carcinogenicity, allergic reactions, and drug sensitization.
The widespread use of antibiotics in livestock production contributes to public health concerns. Bacteria and genes have been found in various animals.
The commercialization of meat grown from cells will be entirely free of antibiotics. It will enable producers to create meat from actual animal muscle tissue, circumventing the need for antibiotics.
As consumers look for alternative Proteins in Asia, producing cultivated meat will provide a high degree of confidence that it is possible to consume antibiotic-free meat.
Animal Welfare

Among the other factors driving the search for traditional meat, animal welfare stands tall as lab meat production starts by taking a small cell sample from a livestock animal such as a cow or chicken and then identifying cells that can multiply.
This innovation reduces animals’ suffering and minimizes conventional agriculture’s environmental burden, contributing to habitat destruction and biodiversity loss.
The projected global consumption of beef and veal will amount to 77.63 metric kilotons by 2032; lab meat will eliminate the need for farming and killing billions of animals annually.
By offering a more humane and sustainable alternative to conventional meat production, cultivated meat is a promising solution to address the growing global demand for protein while minimizing animal harm.
When Will Cultivated Meat Be Available?
A lot has to happen before cell-cultured meat is a primary industry, including regulatory hurdles, investments, global reach, and convincing the meat-loving population to consume cultivated meat as a viable alternative.
The global meat market is expected to grow annually by 6.35% (CAGR 2023-2028), and the global population is expected to reach 10 billion around 2060, leading to an increased demand for meat.
Our growing population, economic growth, and the expanding middle class will fuel the demand further.
As USDA allows lab-grown meat to be sold to US consumers, it will change how meat makes it to our table. However, according to the Good Food Institute, companies today have not reached cost-effective commercial production.
Singapore was the first country ever to approve a cultured meat producthttps://www.statista.com/topics/8043/cultured-meat/. The Singapore Food Agency approved the world’s first cultivated chicken product for sale in December 2020, where it is currently sold in several restaurants, public food stalls, and a butchery.
Food manufacturers in other countries are at various stages of developing regulatory frameworks to permit the sale of cultivated meat.
They are still exploring the viability of cultivated meat production, seeking investments and facilities to ensure lab-grown meat in large quantities in controlled environments.
Cultivated Meat (FAQs)
Did the FDA Approve cultivated meat?
Yes. FDA has provided a 2nd safety nod to cultivated meat, produced without slaughtering animals. However, the companies will require additional approval to market cell-cultivated beef, pork, or seafood.
How much will lab-grown meat cost?
According to the data published by Forbes, Good Meat CEO Josh Tetrick they were stated that 30 million pounds of cultivated meat would cost as much as $650 million.
Will lab-grown meat replace traditional meat?
Lab-grown meat will replace a significant percentage of the meat we eat and not completely take over the meat market.
Is cultivated meat vegan?
Cultivated meat is not vegan, as it is taken from animal cells. However, it is slaughter-free. Thus, some vegans might opt to consume it.
Closing Thoughts
Now that you know what cultivated meat is, how it is produced, and the underlying benefits, it represents a promising leap toward sustainable and ethical food production.
While still in its nascent stages, the prospect of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, alleviating animal suffering, and enhancing food security is compelling and holds the potential to address traditional livestock farming challenges.
As the cell-based meat industry matures, it offers an exciting glimpse into a future where our dietary choices can be more harmonious with the planet and its inhabitants.













