When checking a food label, you’ve likely seen Percent Daily Value (%DV) next to nutrients like calcium, fiber, or sodium. But what is Percent Daily Value exactly? Simply put, %DV helps you understand how much a nutrient in one serving adds to your daily diet.
Based on a 2,000-calorie daily intake, it offers a quick way to compare foods and choose options that meet your nutritional needs. A 5% DV or less means food is low in that nutrient, while 20% or more makes it a high source.
Whether you’re looking to increase vitamins and minerals or cut back on sodium and added sugars, knowing Percent Daily Value can help you make informed choices.
It simplifies nutrition information, so you don’t have to calculate exact nutrient amounts—just check the label and decide what works best for your diet.
What is Percent Daily Value (%DV)?

Percent Daily Value (%DV) is a significant part of nutrition information found on food labels. It represents the percentage of a specific nutrient provided by one serving of a food product compared to the recommended daily intake, making it easier to see how food fits into one’s diet.
The FDA and other agencies use a 2,000-calorie diet as a standard for %DV. While individual needs may vary, this standard helps consumers quickly assess whether a food is high or low in a particular nutrient.
For example, a 5% DV or less product is considered low in that nutrient, while 20% DV or more is high. By checking the food nutrition labels, you can compare products, make better choices, and maintain a balanced diet without calculating exact nutrient amounts.
How is Percent Daily Value (%DV) Calculated?
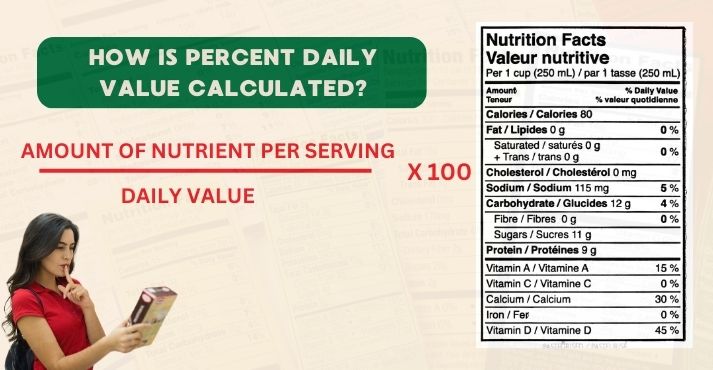
Percent Daily Value (%DV) is calculated using a simple formula: Percent Daily Value (%DV) = (Amount of nutrient per serving / Daily Value) × 100.
For example, if a food product contains 300mg of calcium per serving, and the Daily Value (DV) for calcium is 1,300mg, the calculation would be: (300 / 1300) × 100 = 23% DV.
This means one serving provides 23% of the recommended daily calcium intake. DV in nutrition helps consumers determine if a food is high or low in specific nutrients, making it easier to maintain a balanced diet.
Key Nutrients and %DV
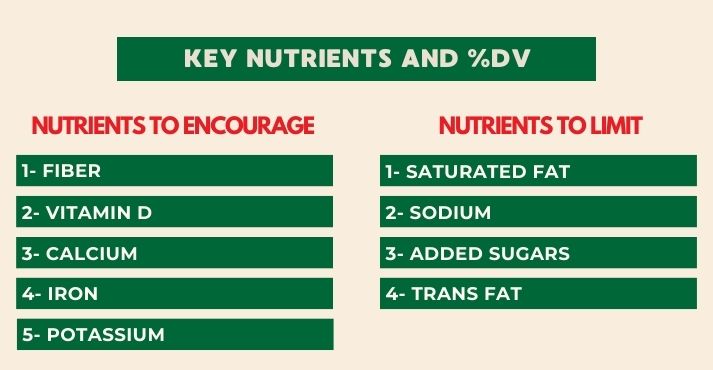
The Percent Daily Value (%DV) helps assess the primary nutrients in your diet. Some nutrients should be consumed more frequently for overall health, while others should be limited to reduce health risks.
Here’s a breakdown of essential nutrients and their recommended daily values:
Nutrients to Encourage
These nutrients contribute to a healthy diet and should be consumed in adequate amounts:
- Fiber – Helps with digestion and promotes heart health. The recommended daily intake is at least 28g per day. Foods with 20% DV or more per serving are considered excellent sources.
- Vitamin D – Supports bone health and immune function. The Daily Value (DV) is 20mcg per day. Since it’s found in limited foods, fortified products and supplements can help meet this requirement.
- Calcium – Essential for strong bones and teeth. The recommended daily intake is 1,300mg, meaning that a food with 130mg of calcium per serving provides 10% of the daily value (DV).
- Iron – Necessary for oxygen transport in the blood. The daily value is 18mg with 20% DV (3.6mg per serving) or more considered a high source.
- Potassium – Helps regulate blood pressure and muscle function. The recommended daily intake is 4,700mg. Many fruits, vegetables, and legumes are rich sources of potassium.
With the increasing emphasis on transparency in the food industry, food manufacturers must now provide clearer nutrition and detailed ingredient labels, making it easier for consumers to identify nutrient-dense foods and better understand what goes into their meals.
Nutrients to Limit
Some nutrients should be consumed in moderation to maintain good health:
- Saturated Fat – Excess intake can raise cholesterol levels and increase heart disease risk. Limiting saturated fat to no more than 20g per day is recommended.
- Sodium – High sodium intake is linked to high blood pressure. The DV is 2,300mg daily, meaning foods with 5% DV (115mg) or less are low in sodium, while 20% DV (460mg) or more is considered high.
- Added Sugars – Excess sugar intake leads to obesity and diabetes. The recommended limit is 50g per day, so a product with 25g of added sugar per serving provides 50% DV.
- Trans Fat — Unlike other nutrients, there is no %DV for trans fat, which is recommended to be avoided entirely due to its negative impact on heart health.
By checking %DV and nutri-score, consumers can decide to increase beneficial nutrients while limiting unhealthy ones for a balanced diet.
Conclusion
Percent Daily Value (%DV) helps you assess a food’s nutritional content. It shows whether a product is high or low in essential nutrients, making it easier to make informed dietary choices.
Based on a 2,000-calorie diet, %DV makes it easy to compare foods without complex calculations.
Focusing on nutrients to encourage, such as fiber, calcium, and vitamin D, can support overall health, while limiting sodium, saturated fat, and added sugars helps maintain a balanced diet.
Checking the nutrition information on food labels allows you to make choices that align with your health goals.





























