3D food printing is transforming traditional restaurant kitchens worldwide.
3D printing foods give food manufacturers more significant control over the product’s final shape, nutrition, and taste characteristics. The main attraction of 3D printing is personalization and customization, which lures big F&B players into this space.
But do you know what 3D-printed food is?
3D printing is depositing, joining, or solidifying material under computer control to form a three-dimensional object using CAD or a 3D model.
3D printing has numerous applications in the food industry that may enhance diversity, quality, healthiness, and sustainability. It is set to revolutionize food production by creating food efficiently and at a lower cost.
This blog will examine everything you need to know about 3D-printed food.
- How Does 3D Food Printing Work?
- Types of Ingredients Used in 3D Printing
- Examples of 3D-Printed Food
- Pros and Cons of 3D Food Printing
- Technological Advancements in 3D Food Printing
- Future Trends and Predictions
How Does 3D Food Printing Work?

You may wonder how 3D food printing could work if you are new to this technology.
Initially, 3d printing food could only create sculptures and designs, but as foodtech has evolved, it is possible to create pasta, lab-grown meat, and meals with personalized nutrition.
3D food printing involves the layer-by-layer deposition of edible materials to create three-dimensional structures.
The process typically begins with creating a digital model of the desired food item. Specialized 3D printers then follow this model, extruding or depositing food materials onto a printing surface, often in paste or powder form.
The layers solidify or fuse, forming the final edible product. Ingredients can include various food components like proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
This technology allows for precise textures, shapes, and nutritional value customization, paving the way for personalized and efficient food production.
Key technologies and methods involved in 3D food printing include:
- Digital modeling
Designing a digital representation of the food item guides the 3D printer in creating accurate structures layer by layer.
- Extrusion systems
These systems push or extrude edible materials, often in paste or powder form, through a nozzle for precise deposition.
- Material science
Developing edible materials compatible with 3D printing, considering taste, texture, and nutritional aspects for optimal printing results.
- Layering techniques
Printing successive layers accurately and efficiently, ensuring proper adhesion and consistency in the final 3D-printed food product.
- Post-processing methods
Techniques like heat application or cooling to enhance the texture, taste, and overall quality of the printed food items.
- Bioprinting
It involves printing with living cells and exploring the potential for creating sustainable and customized food products with unique health benefits.
- Sensors and monitoring
Incorporating sensors for real-time monitoring of the printing process, ensuring precision, and adjusting parameters as needed for optimal results.
Types of Ingredients Used in 3D Printing
A wide range of food ingredients with proteins, starch, and fats can be used for food printing. Some of the most common 3d food printer ingredients include:
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Fats and Oils
- Fibers
- Hydrocolloids
- Nutrients and Vitamins
- Sweeteners
- Water-based Mixtures
3D-printed food ingredients need to have two essential things to hold the shape of the finished product: viscosity and mechanical strength.
Examples of 3D-Printed Food
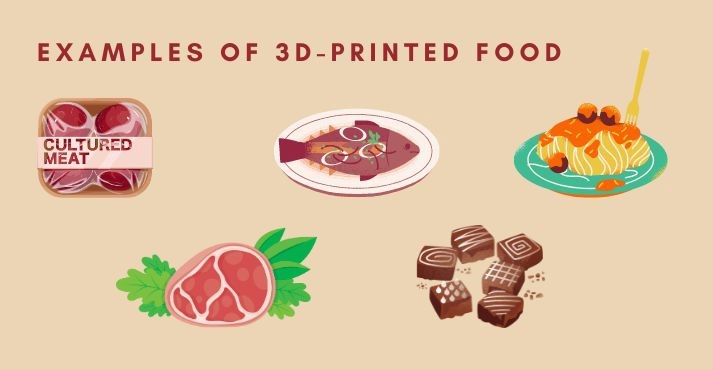
Here are some 3D-printed food examples:
- Cultured meat: Creating unique textures and presentations, 3D printing technology aligns with sustainable practices, offering innovative ways to showcase lab-grown or alternative proteins on menus.
- Plant-based meat: 3D printing helps chefs craft intricate plant-based meat structures, enhancing visual appeal and transforming the dining experience. It allows for creative expression while meeting the rising demand for alternative protein sources.
- Chocolate: Chocolatiers leverage 3D printing to design intricate chocolate sculptures and custom-shaped treats. This precise technology offers chefs new possibilities for artistic expression and elevates the presentation of chocolate-based desserts.
- Fish: Chefs experiment with 3D printing for fish substitutes, exploring novel textures and shapes. This application caters to seafood alternatives, addressing sustainability concerns and offering unique culinary experiences for diners.
- Pasta: 3D printing transforms pasta creation by enabling chefs to craft intricate designs and customized shapes. This innovation in pasta-making adds a layer of creativity to traditional dishes, redefining pasta’s visual and textural aspects.
Pros and Cons of 3D Food Printing
From personalization to sustainability, there are some great benefits that 3D food printing offers. However, some drawbacks are propelling the growth of the 3D food printing industry.
Pros of 3D Food Printing
- Customization
3D-printed food allows precise control over ingredients, textures, and shapes, enabling tailored culinary experiences for individuals with specific dietary preferences, restrictions, or cultural requirements.
- Personalized Nutrition
Tailoring nutritional content in 3D printed food enables personalized health goals, accommodating diverse dietary needs, optimizing nutrient intake, and addressing individual health conditions more effectively than mass-produced alternatives.
- Easier swallowing
Adapted textures and structures in 3D-printed food can cater to individuals with swallowing difficulties, providing a safer and more enjoyable dining experience for elderly or medically compromised individuals.
- Plant-based meat
3D printing facilitates the creation of intricate plant-based meat substitutes with realistic textures and flavors, contributing to sustainable and cruelty-free alternatives to traditional animal products.
- Reducing food waste
Precise ingredient deposition in 3D printing minimizes excess and ensures efficient use of raw materials, reducing food waste at both the production and consumer levels.
- Unconventional food consumption
Creative designs and novel structures made possible by 3D printing encourage innovative culinary experiences, challenging traditional food presentation and consumption notions.
- Space travel
3D-printed food technology holds promise for space exploration, offering a compact and efficient means of producing nutritionally optimized meals in resource-limited environments and ensuring sustenance for astronauts during extended missions.
Cons of 3D Food Printing
- Costly equipment
The initial investment and maintenance expenses for 3D food printing technology are high, limiting accessibility and adoption, particularly for smaller businesses or individuals with budget constraints.
- Limited flavor complexity
Current technology needs to work on replicating the intricate and nuanced flavors achieved through traditional cooking methods, hindering the diversity and richness of taste in 3D-printed foods.
- Dependency on waw material quality:
The quality of 3D-printed food heavily relies on the raw materials used. Inconsistent or subpar ingredients can affect the printed food’s taste, texture, and quality.
- Ethical and cultural concerns
The shift to 3D-printed food raises ethical questions regarding the artificiality of the process, potentially clashing with cultural values and preferences tied to traditional food preparation and consumption methods.
Technological Advancements in 3D Food Printing

Multidisciplinary knowledge and technological developments have advanced 3D food printing in recent years.
Here are the latest technological advancements in the 3d print food market:
- Artificial Intelligence
AI integration in 3D food printing involves utilizing artificial intelligence algorithms to optimize food design, texture, and flavor.
It enables personalized nutrition, efficient recipe generation, and enhanced culinary creativity, pushing the boundaries of innovative and customizable food production.
- Customized Nutrition Printing
Companies have been working on 3D food printers that can create customized nutritional profiles based on individual dietary needs, health requirements, and preferences. It integrates AI algorithms to analyze user data and recommend specific food formulations.
- Bioprinting for Alternative Proteins:
Some companies are exploring 3D bioprinting to create plant-based or lab-grown meat alternatives. While this is not directly related to AI, optimizing the printing process and developing realistic textures and flavors could benefit from AI algorithms.
Here are some notable breakthroughs achieved in 3D food printing:
- Diverse Range of Materials: A breakthrough in 3D-printed food involves using a diverse range of materials beyond traditional ingredients. This innovation expands the possibilities for creating novel textures, structures, and flavors. From edible gels to alternative protein sources, it unlocks new culinary avenues, driving creativity and addressing various dietary needs in personalized food printing.
- Integration of AI and Sensors: This synergy allows real-time monitoring and adjustment of printing parameters based on data feedback. Precise control enhances food quality, consistency, customization, and adaptive and efficient 3D printing.
- Reduces Food Wastage: Precision in ingredient usage, enabled by accurate portioning through AI algorithms, minimizes excess materials. This innovation aligns with sustainability goals, enhances production efficiency, and contributes to a more environmentally conscious approach to food manufacturing.
Future Trends and Predictions
3d printing edible food is poised to change the food and beverage industry. The global 3D food printing market is predicted to grow to around USD 1.65 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 16.12% between 2022 and 2030.
Anticipated trends include personalized nutrition, as printers tailor meals to individual dietary needs, and sustainable practices, reducing food waste through precise ingredient utilization.
Moreover, the technology may redefine culinary artistry by enabling intricate, customizable designs and textures.
As accessibility and affordability increase, 3D food printing is expected to democratize culinary creativity, offering new possibilities for chefs and home cooks to craft visually stunning, flavorful, and nutritionally optimized dishes.
Moreover, 3D printing production can be situated closer to the consumer location, and manufacturing organizations leveraging this technology can build shorter, stronger, and more resilient food supply chains.
Advancements in 3D printing technology have greatly expanded its potential applications in the food and beverage industry.
3D-printed Food (FAQs)
Can you eat 3d printed food?
Yes, it is possible to eat 3D-printed food. 3D printing technology has been applied to the culinary world, allowing for the creation of intricate and customized shapes and designs with edible materials.
Is 3D-Printed Food Safe?
The safety of 3D-printed food depends on several factors, such as:
- Food-grade materials
- Hygiene and sterilization
- Regular compliance
- Research and testing
How long does it take to 3D print food?
Simple designs take 1 to 2 minutes, detailed designs take 3 to 7 minutes, and more intricate designs take even longer. The printing speed, layer thickness, and other settings influence the printing time.
Conclusion
3D-printed food technology can transform the food and beverage industries for the better. If utilized fully, it could make a massive difference in food waste and environmental impacts.
This innovative method allows precise control over ingredients and nutritional content, catering to individual dietary needs and preferences.
While the technology is still evolving, its potential to address food security challenges, reduce waste, and enhance culinary creativity is promising. The ability to transform raw materials into intricate, customized shapes opens up new possibilities for presentation and taste experiences.
Now that you know what 3D-printed food is, it is taking the world by storm. As 3D printing technology continues to evolve and develop, it holds the potential to revolutionize the way we produce, consumes, and experience meals.





























